Targeting Strategies for Beginners: How to Segment and Approach Your Audience

One of the reasons why going to a restaurant is awesome is the simplicity of the interaction. But, imagine if the menu wasn’t grouped into different sections. Instead, the wines, entrees, desserts, and mains are all scrambled together, forcing you to read the whole thing one by one.
Needless to say, you’d probably question the owner’s sanity and walk out of the establishment. Creating a marketing campaign is similar to this situation, but instead of picking a meal, you’re trying to find the people you want to advertise to.
And unfortunately, your menu is usually scrambled.
Targeted marketing and segmentation can help unscramble your menu by grouping your potential customers together, making it easier to create appealing content for them. This article will cover this concept and give you tips on targeting your ads for your audience.
Breaking Down Targeted Advertising and Customer Segmentation
Before delving into the targeted ads, let’s look at segmentation. The process of segmentation consists into separating your potential customers into groups based on common traits.
Segmentation can occur at very broad and narrow levels. You can group people into segments based on broad characteristics like GEO or narrow it down by dividing customers based on intricate user activity targeting option.
Segmentation takes time, so you need to check all elements such as location, OS, device type, internet provider, and many others in order to create the right categories. What targeting options are available?
As a general rule of thumb, broader segments tend to have lower conversion rates and ROI, but are faster to deploy. On the other hand, defining a specific group may be very profitable, but this process requires some work on your behalf.
At a granular level, segmentation can lead to the development of buyer personas, which are fictional depictions of your ideal customer. Remember to always name your segments and buyer personas in order to help you use them and reference them during your marketing campaigns!
Once you have segmented your audience, you’ll want to start targeting your ads. Targeted marketing consists of creating campaigns based on these different segments. This can mean using specific channels, formats, content, wording, ad scheduling, or any other elements that may help focus on one specific segment.
Some elements you may want to include when creating segments and targeted ads include. You can take these elements from your current audience’s statistics:
- The demographics of your customer
- Geolocation
- Income level (See also: What Tier of Traffic to choose)
- Stage of the buyer’s journey (Maybe your customer have registered but is not active yet or have started but is not active anymore)
- Buying cycle (How often a certain product is purchased)
- The customer’s preferred communication channel
- Users’ interests
Common Targeting Strategies Found Today
There is an infinite collection of creative ways to employ targeted ads. We’ve listed some of the most common and profitable models below to help inspire your first campaigns. However, finding the ideal structure will depend on your business, so don’t be afraid to invest time to crack the code!
Broad Marketing Strategy
Broard (or Mass) marketing is the lowest possible level of targeting. You can target every single possible person you can reach or you can focus on extremely large groups. Broad segmentation is often preferred here, but the results represent multiple demographics and may be interpreted in a variety of ways.
Companies that are trying to increase visibility such as games or tangible goods may benefit from mass marketing. That said, it’s not ideal for platforms that want to focus on increasing sales or generating higher profits quickly.
Pros
- More affordable
- Appeals to the masses
- Easier to create than niche campaigns
Cons
- May only resonate positively in some areas
- Doesn’t focus on one client or customer group
- Changes in the marketing landscape are not taken into consideration
Concentrated Targeting Strategy
Concentrated advertising is targeted ads in their purest form. You need to identify a group of potential customers that are more likely to convert than the average consumer. For instance, app developers that only work with iOS devices can focus on the only valuable segment: Apple products.
Unlike mass media, concentrated targeting is not ideal for advertisers that want to create awareness or want to increase brand visibility.
Pros
- Can choose from a collection of elements to focus on
- Allows creativity because you are working with the audience you already know
- It’s cost-effective
Cons
- Limits your potential reach and exposure
Geographic Strategy
Geographic segmentation, sometimes referred to as geo-targeting or simply GEO, focuses on delivering ads to an audience based on their location, country or language. Dating platforms that only work in certain areas can employ geo-targeting to help focus their efforts on areas with better performance.
Keep in mind that GEO campaigns are harder to optimize, plus you may increase costs if done wrong.
Pros
- Focus on high-profit areas
- Gain local relevance
- If done correctly, may increase ROI
Cons
- Tricky optimizations
- Two or more areas may compete with each other and increase costs
Retargeting
There are many cases where consumers actually reach one of your landing pages or download your app, but never complete the desired action. Retargeting campaigns help identify these scenarios, allowing you to segment your audience based on prior encounters with your brand. Then, you can create a plan to reignite their interest and drive them to complete their initial intention.
Some argue that retargeting may breach customer privacy, which means that consumers may frown upon your brand. At the same time, increased visibility may also result in loss of exclusiveness.
Pros
- Pursue prospects that already showed interest in your content
- Delivers attractive promotions to consumers
Cons
- Exposed visibility may result in reduced exclusiveness
Content-Based Targeting Strategy
Content-based targeting (also content/contextual targeting) is a two-pronged process that works best with native ads and push notifications because you are reaching the audience that is already interested in similar products/services. You need to adjust the images and other creative elements you employ to target a certain audience or related websites.
Then, you can employ an additional targeting method like geographic segmentation to create multiple mini-campaigns that run simultaneously in an ultra-targeted environment. The most effective campaign tend to focus on aspects that help target the customer at the right time.
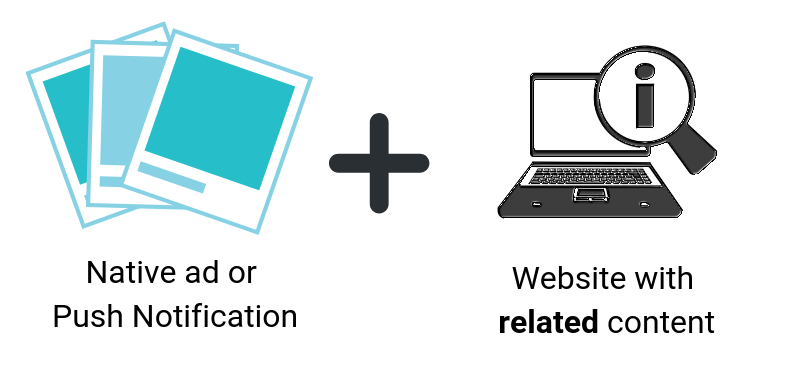
For instance, considering the stage of the sales funnel. Customers that are close to the top of the funnel need broad, informative ads. Consumers that are already close to the bottom require specific content that shows them the benefits and details downloading your app or using your platform.
Pros
- Generate an emotional reaction
- Appear on the websites with related content
- Can limit the audience with various warnings (For example, betting companies can specify that their product is 18+ only)
Cons
- Requires engaging content and multiple sets of strong creatives
- It requires significant money and time investments
There are so many more targeting strategies you can employ, but these are the most beginner-friendly. What targeting strategies do you employ?
>> Launch Campaign <<



